equals와 hashCode는 왜 같이 재정의해야 할까?
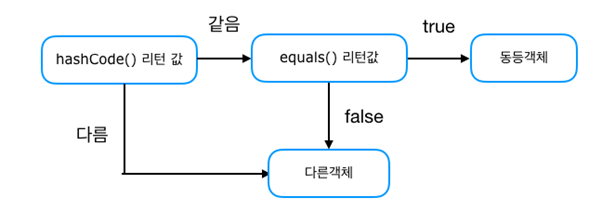
hash 값을 사용하는 Collection(HashMap, HashSet, HashTable)은 객체가 논리적으로 같은지 비교할 때 아래 그림과 같은 과정을 거친다.

hashCode 메소드의 반환값을 이용해서 검색의 범위를 확 줄여버리고, 해당 부류 내에 존재하는 데이터의 내용 비교는 equals 메소드를 통해서 진행한다.
Object 클래스의 hashCode 메소드는 인스턴스가 다르면 구성 내용에 상관없이 전혀 다른 해시값을 반환하도록 정의되어 있다. equals 메소드도 내용 비교가 아닌, 참조값만 비교하도록 정의되어 있다. 따라서 이 두 메소드를 적절히 오버라이딩해야 두 개의 인스턴스를 동일한 인스턴스로 인식시킬 수 있다.
equals와 hashCode 재정의 예시
String
String 클래스에 정의된 hashCode 메소드는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public int hashCode() {
int h = this.hash;
if (h == 0 && this.value.length > 0) {
this.hash = h = this.isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.hashCode(this.value) : StringUTF16.hashCode(this.value);
}
return h;
}
|
String 클래스에 정의된 equals 메소드는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
} else {
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String aString = (String)anObject;
if (this.coder() == aString.coder()) {
return this.isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.equals(this.value, aString.value) : StringUTF16.equals(this.value, aString.value);
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
Arrays
Arrays 클래스에 정의된 hashCode 메소드는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public static int hashCode(Object a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (Object element : a)
result = 31 * result + (element == null ? 0 : element.hashCode());
return result;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public static boolean equals(int[] a, int[] a2) {
if (a == a2) {
return true;
} else if (a != null && a2 != null) {
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length) {
return false;
} else {
return ArraysSupport.mismatch(a, a2, length) < 0;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
|